Four Innovation Labs. One Mission: A Resilient Africa.
Resilience Innovation Labs (RILabs) are dynamic regional hubs that drive locally led innovation, research, and practical solutions to Africa’s toughest challenges from climate change to chronic conflict and urbanization.
What RILabs Do ?
Resilience Innovation Labs (RILabs) are dynamic regional hubs that drive locally led innovation, research, and practical solutions to Africa’s toughest challenges from climate change to chronic conflict and urbanization.
Incubate Local Solutions
Identifying and supporting community-driven innovations
Bridge Research and Action
Engaging students, faculty, and local innovators
Build Capacity
Offering mentorship, training, incubation, and seed funding
Scale What Works
Sharing proven solutions with similar vulnerable communities
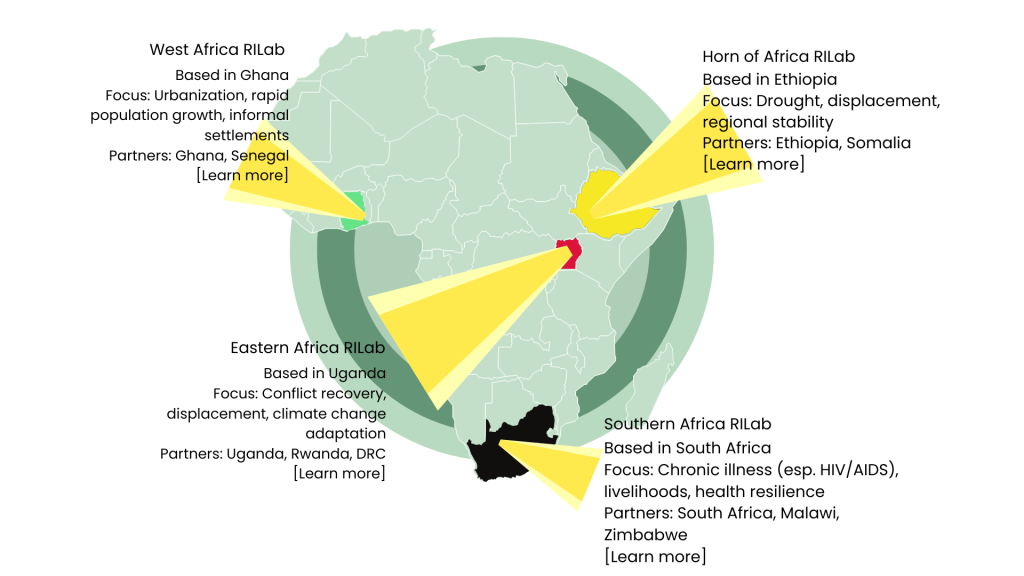
Where We Work
Resilience isn’t just surviving, it’s the capacity to thrive in the face of challenge.
Our 4-Step Framework
In RAN’s context, resilience is the ability of individuals, communities, and systems to:
Purpose of the Framework
The RAN Resilience Framework was designed to:
Understand the root causes of vulnerability and exposure
Identify what helps people and systems withstand, adapt to, and recover from shocks
Define resilience dimensions and indicators for effective measurement
Guide evidence-based interventions that drive real, long-term change
Learn, Apply and Scale
This framework is actively used to guide RAN’s work and help stakeholders across Africa design smarter, more impactful resilience strategies.


